Deploying Fortify SSC 24.4 on Kubernetes Using Helm
Deploying Fortify SSC 24.4 on Kubernetes Using Helm
This guide provides a detailed, step-by-step process for deploying Fortify SSC 24.4 on Kubernetes using Helm.
1. Prerequisites/Requirements
Before proceeding with the deployment, ensure the following prerequisites are met:
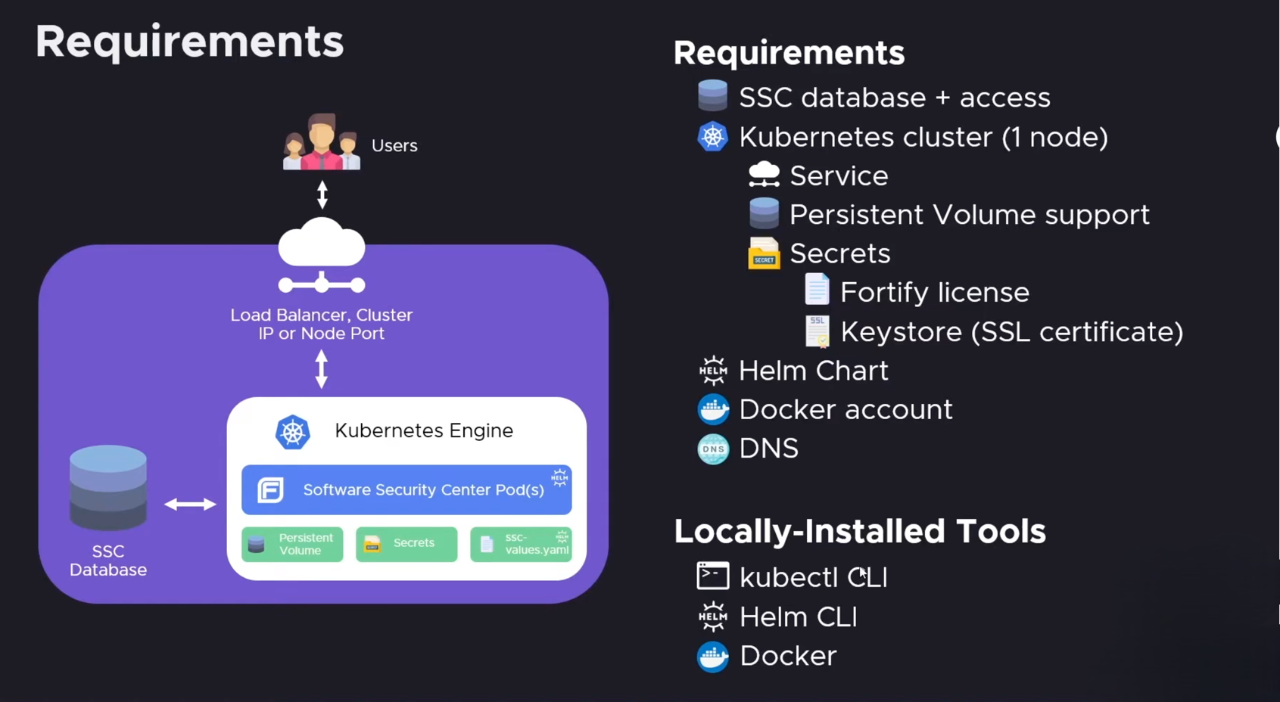
2. Prepare the Environment
Install Prerequisites
Ensure the following tools are installed locally on your system:
-
kubectl CLI
Install using the official documentation: Install kubectlkubectl version --client -
Helm CLI
Install using the Helm website: Install Helmhelm version -
Docker
Install Docker from the official website: Install Dockerdocker --version
Using Minikube for Local Kubernetes
If you do not have a Kubernetes cluster and want to run Kubernetes locally, you can use Minikube:
-
Install Minikube
Follow the installation guide: Install Minikubeminikube start -
Enable Load Balancer
Minikube supports Load Balancer services via the tunnel command:minikube tunnel -
Set Minikube Context for kubectl
Ensurekubectlis pointing to Minikube:kubectl config use-context minikube -
Create Alias for Minikube’s kubectl
Minikube provides its own version ofkubectl. Create an alias to use it seamlessly:alias kubectl="minikube kubectl --"Now, you can use
kubectlcommands directly while pointing to Minikube’s Kubernetes cluster.
Create Docker Secret
Ensure Kubernetes can pull images from private Docker registries:
kubectl create secret generic regcred \
--from-file=.dockerconfigjson=.docker/config.json \
--type=kubernetes.io/dockerconfigjson
Open Firewall Ports
Allow necessary ports for Fortify SSC and SQL Server communication:
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=8443/tcp --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=1433/tcp --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
3. Set Up the SQL Server Database
Pull SQL Server Image
Download the latest SQL Server image:
docker pull mcr.microsoft.com/mssql/server:2022-latest
Run SQL Server Container
Start the SQL Server container:
docker run -e 'ACCEPT_EULA=Y' -e 'SA_PASSWORD=P@ssw0rdH' \
-p 1433:1433 --name mssql-server -d mcr.microsoft.com/mssql/server:2022-latest
Connect to SQL Server
Verify connectivity:
docker exec -it mssql-server /opt/mssql-tools/bin/sqlcmd -S localhost -U sa -P 'P@ssw0rdH'
4. Prepare Fortify SSC Secrets
Create Secrets Directory
Navigate to the Helm chart directory and create a secrets folder:
cd Fortify/helm
mkdir secrets
Add Required Files
Place the following files into the secrets/ directory:
fortify.licensessc.autoconfig.yamlssc-kube.crtssc-kube.jksssc-kube-pass
ssc.autoconfig.yaml File
Create the ssc.autoconfig.yaml file as shown below. This file configures SSC database and application settings. Example:
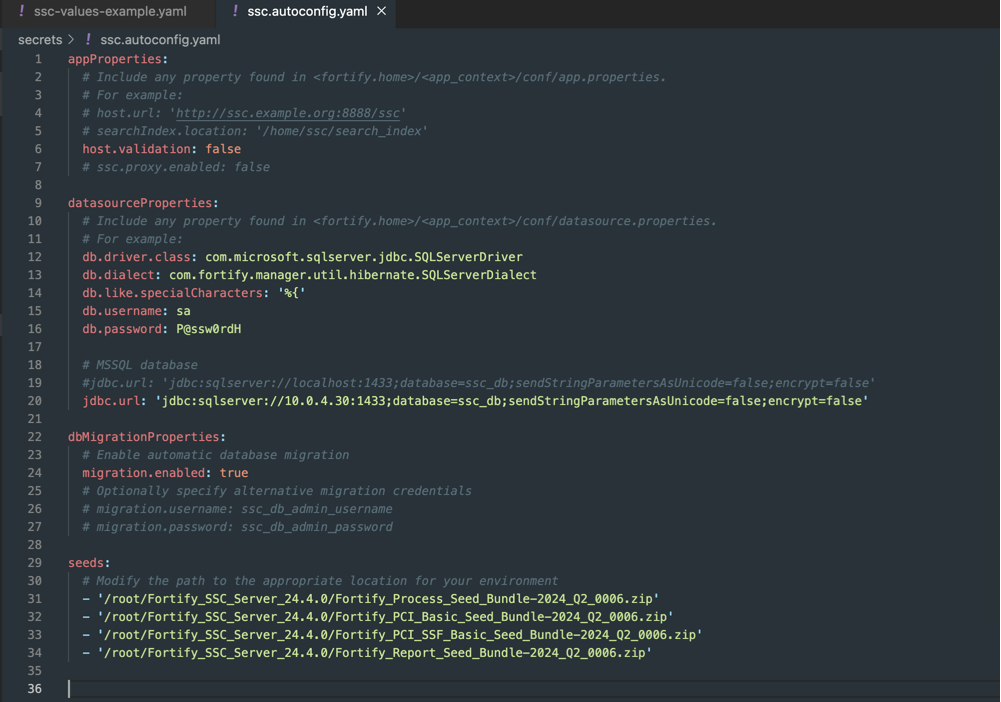
Ensure the following fields are set correctly:
db.username: Username for SQL Server (e.g.,sa)db.password: Password for SQL Server (e.g.,P@ssw0rdH)jdbc.url: Update the IP and database name to your environment.
ssc-values-example.yaml File
Prepare the ssc-values-example.yaml file to configure the Helm chart deployment. Example:
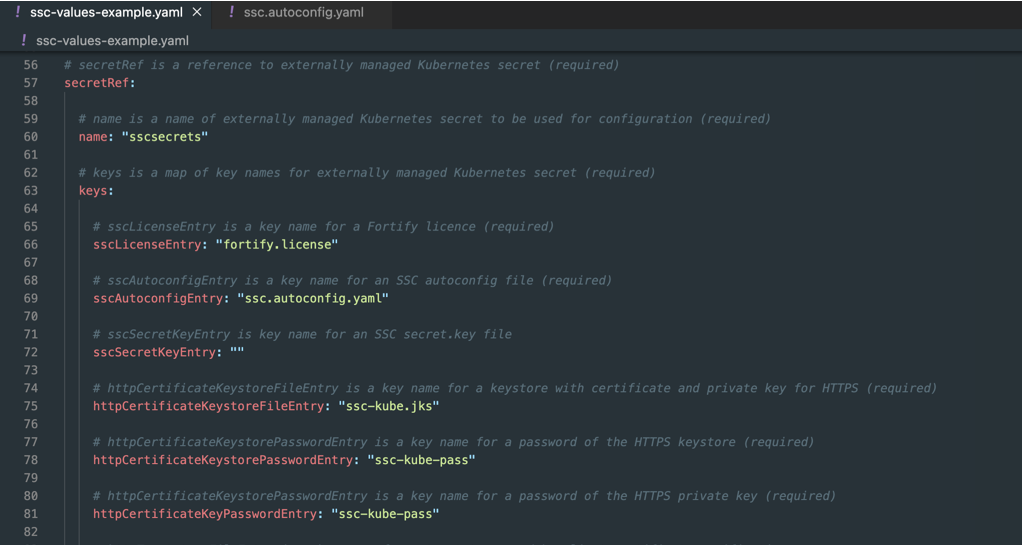
Pay attention to these fields:
secretRef.name: Name of the Kubernetes secret (e.g.,sscsecrets).- Key entries for license files, keystore, and database configuration.
Create Kubernetes Secret
Package the secrets into Kubernetes:
kubectl create secret generic sscsecrets --from-file=secrets/
Verify the secret:
kubectl describe secret sscsecrets
5. Pull Fortify SSC Docker Image
Log In to Docker
Authenticate with Docker Hub:
docker login
Pull the SSC Image
Download the SSC image:
docker pull fortifydocker/ssc-webapp:24.4.0.0000
Create Docker Registry Secret
Create a Kubernetes secret:
kubectl create secret docker-registry regcred \
--docker-server=https://index.docker.io/v1/ \
--docker-username= \
--docker-password=
6. Deploy Fortify SSC 24.4 Using Helm
Pull Fortify SSC Docker Image
Download the SSC Docker image:
docker pull fortifydocker/ssc-webapp:24.4.0.0000
Create Docker Registry Secret
Create a Kubernetes secret for Docker registry authentication:
kubectl create secret docker-registry regcred \
--docker-server=https://index.docker.io/v1/ \
--docker-username=<your-username> \
--docker-password=<your-password>
Install the Helm Chart
Run the Helm command to install SSC:
helm install ssc ssc-1.1.2420000+24.4.0.0000.tgz -f ssc-values-example.yaml
7. Verify the Deployment
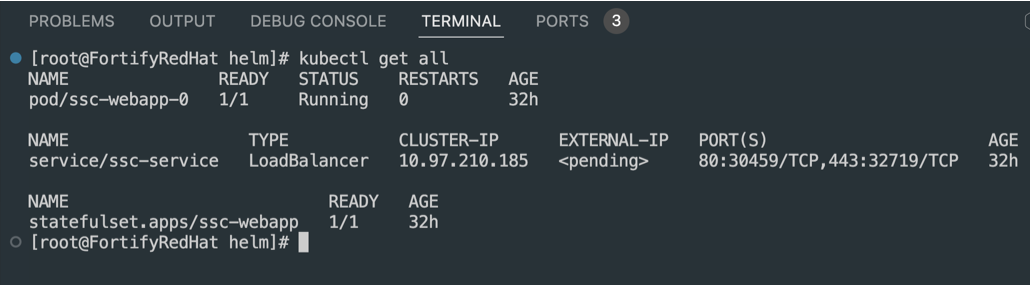
Check Kubernetes Resources
Ensure SSC is running:
kubectl get all
Example output:
Inspect SSC Pod
Check the pod details:
kubectl describe pod ssc-webapp-0
View Logs
View pod logs to troubleshoot issues:
kubectl logs statefulset.apps/ssc-webapp
8. Access Fortify SSC
Local Access via Port Forwarding
Forward the SSC port locally using VS Code terminal or CLI:
kubectl port-forward ssc-webapp-0 8443:8443
Navigate to the following URL:
URL: https://localhost:8443/ssc
Troubleshooting
- If the service does not start:
- Check Kubernetes events:
kubectl describe service ssc-service - Verify Docker image availability.
- Check Kubernetes events:
- If
LoadBalancerisPending, configure MetalLB or useNodePort.